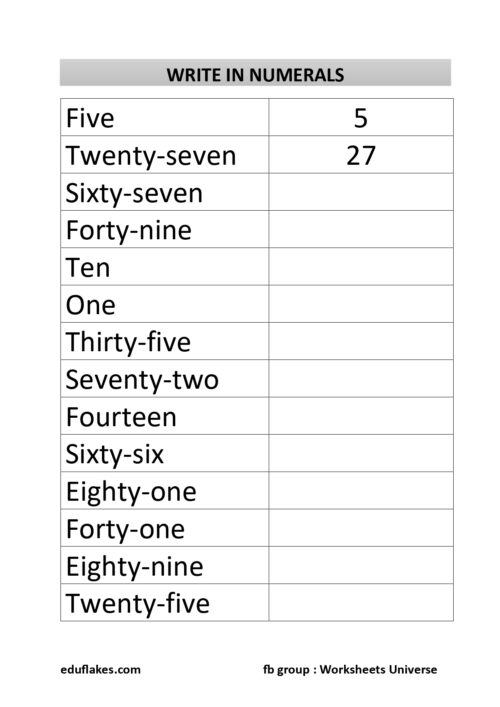
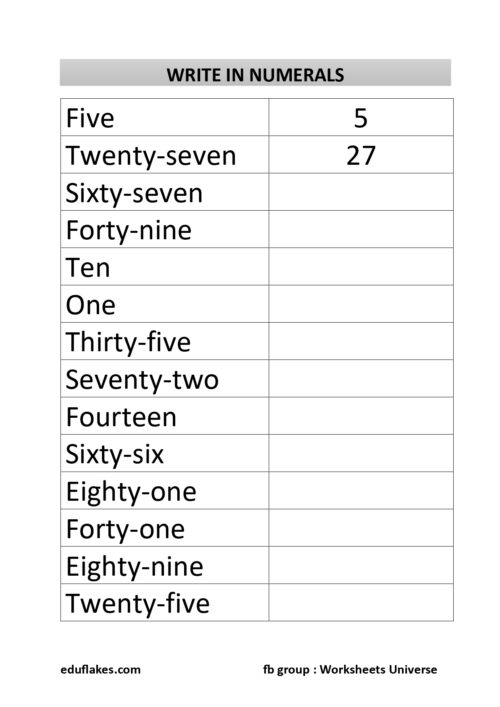
Numbers are an essential part of our daily lives, and understanding their sequence is crucial for young learners. Concepts like “before,” “after,” and “between” help children develop number sense and logical thinking. These concepts form the foundation for arithmetic operations and problem-solving skills. In this article, we will explore these fundamental concepts, why they are important, and how educators and parents can teach them effectively.

What Does “Before,” “After,” and “Between” Mean?
Before we dive into teaching methods, let’s clarify what these terms mean in a numerical context:
- Before: A number that comes earlier in the counting sequence.
- After: A number that follows another number in the sequence.
- Between: A number that lies in the middle of two given numbers.
For example, in the sequence 1, 2, and 3:
- 1 comes before 2.
- 3 comes after 2.
- 2 is between 1 and 3.
The Importance of Learning Number Sequences
Understanding numerical order helps children:
- Develop counting skills: Recognizing which numbers come before or after improves counting accuracy.
- Enhance logical thinking: Identifying numbers between two values sharpens analytical abilities.
- Prepare for advanced math: Addition, subtraction, and number patterns rely on number sequences.
- Improve problem-solving: Recognizing missing numbers in a sequence is an early form of logical reasoning.
Teaching Strategies for Before, After, and Between
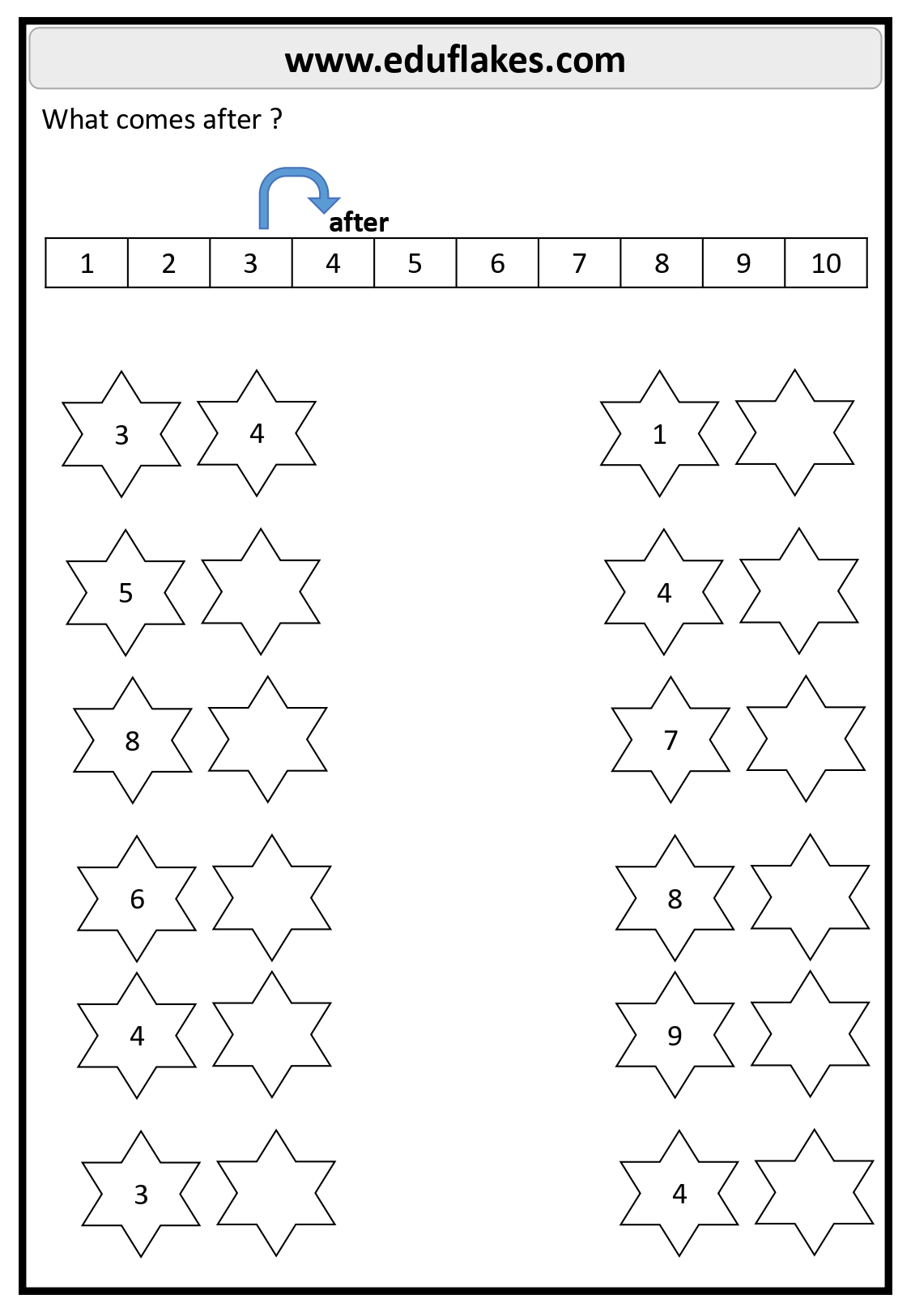
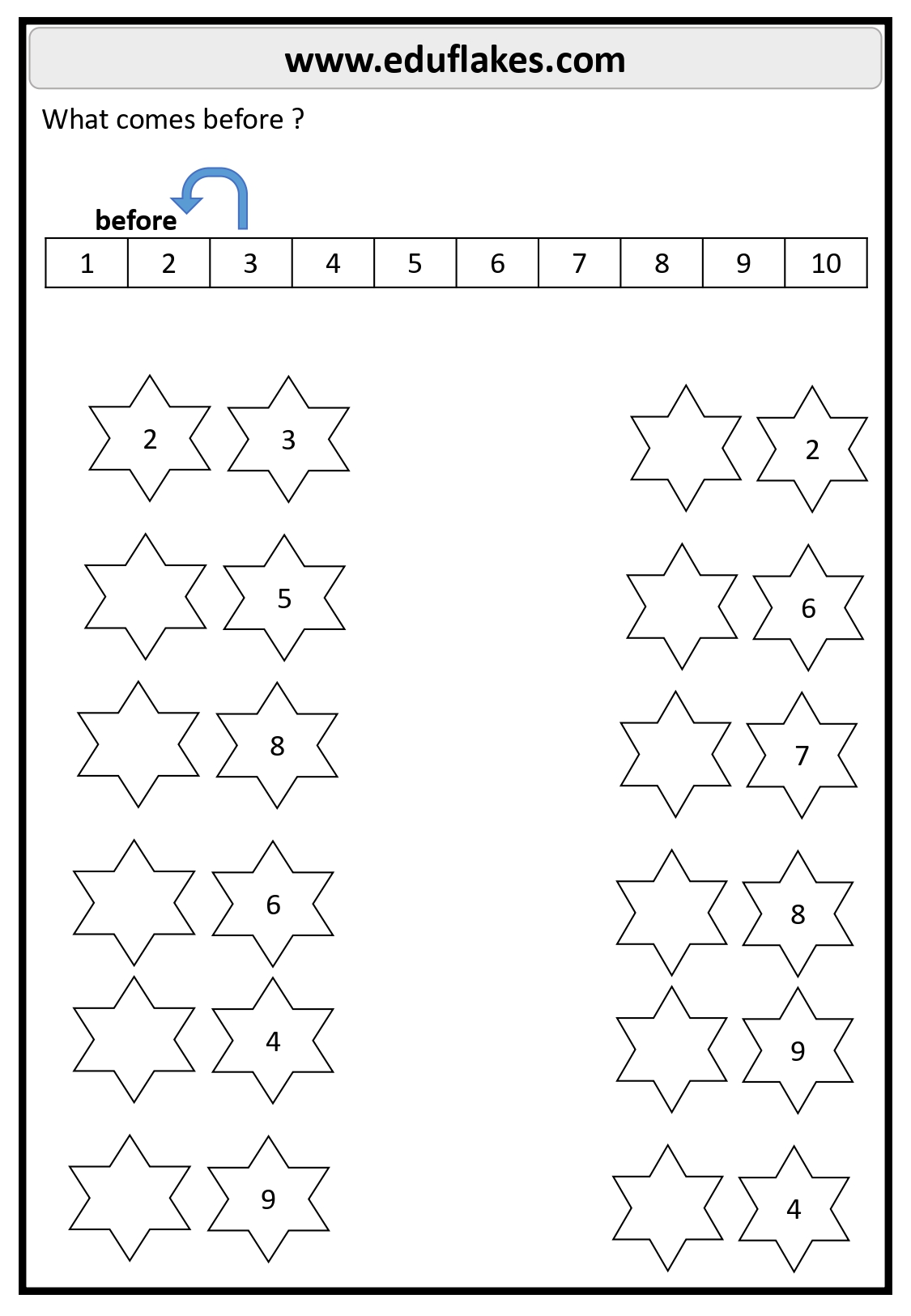
1. Using Number Lines
A number line visually represents numerical order and helps children see patterns. For example:
- Place a marker on number 5 and ask: “What number comes before 5?” (Answer: 4)
- Ask: “What number comes after 5?” (Answer: 6)
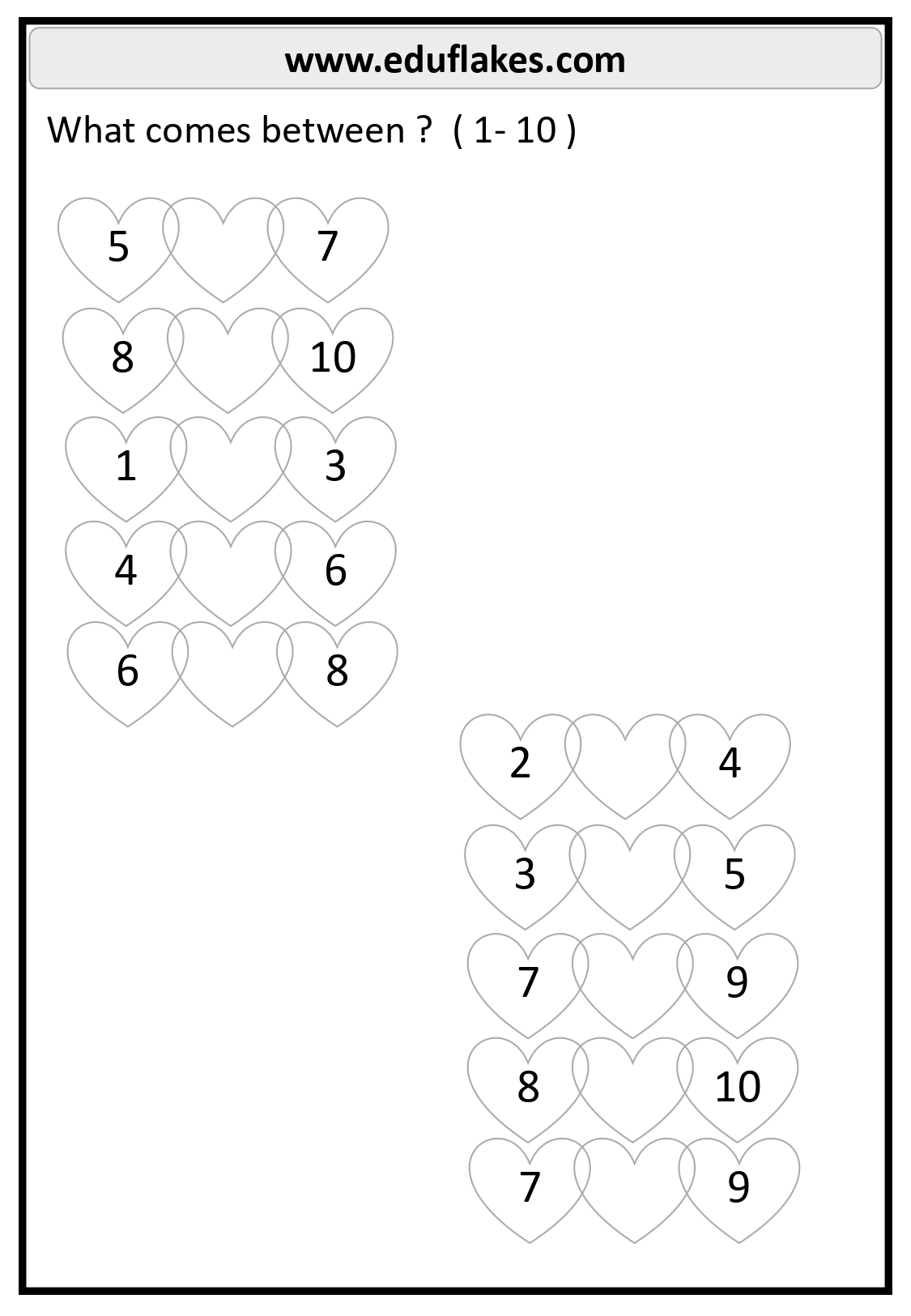
- Find a missing number between two points, such as “What number is between 3 and 5?” (Answer: 4)
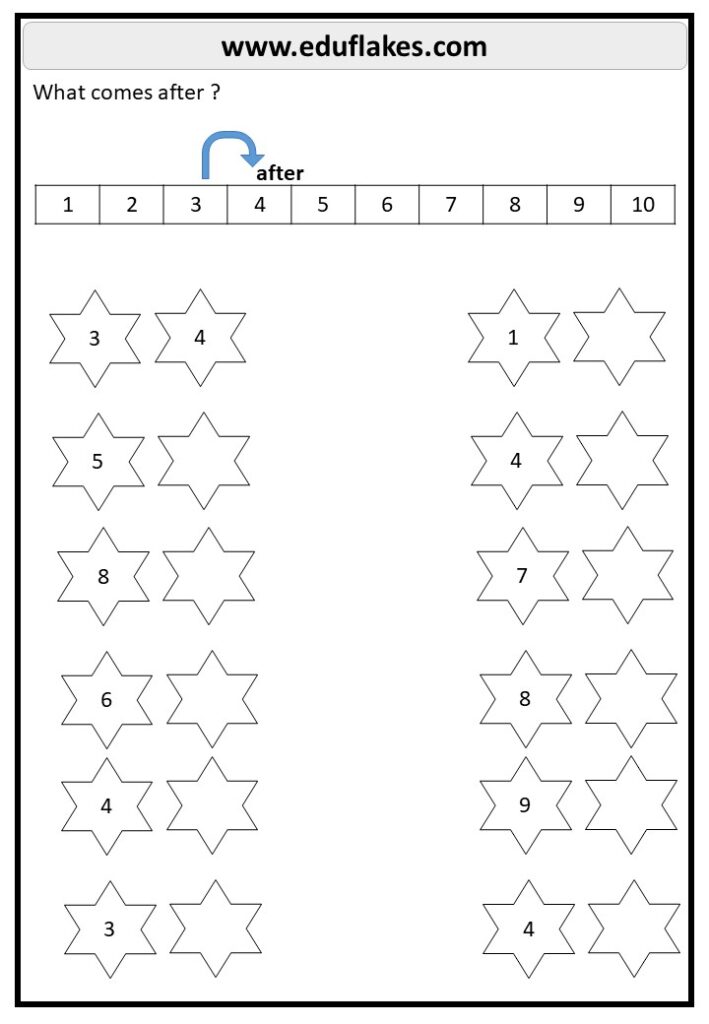
2. Counting Exercises
Encouraging children to count forward and backward helps reinforce number sequences. Activities include:
- Counting from 1 to 10 and back from 10 to 1.
- Skipping numbers and asking children to fill in the blanks, e.g., “1, 2, _, 4, 5. What number is missing?”
- Using songs and rhymes to make counting engaging.

3. Worksheets and Practice Activities
Worksheets help reinforce learning through practice. Some exercises include:
- Tracing numbers to understand order.
- Filling in missing numbers.
- Matching numbers with their correct “before” and “after” counterparts.
4. Using Everyday Examples
Applying concepts in daily activities makes learning more meaningful:
- “We are at house number 5. What house number comes before?” (Answer: 4)
- “What number comes after today’s date?” (If today is the 15th, tomorrow is the 16th.)
- “Can you find the number between 7 and 9 in your toy set?”
5. Interactive Games
Children learn best through play. Some fun games include:
- Number puzzles: Matching numbers with their correct position.
- Flashcards: Showing a number and asking what comes before or after.
- Board games: Using dice rolls to teach number sequences naturally.
Examples for Different Number Ranges
1-10
- Before 3: 2
- After 5: 6
- Between 4 and 6: 5
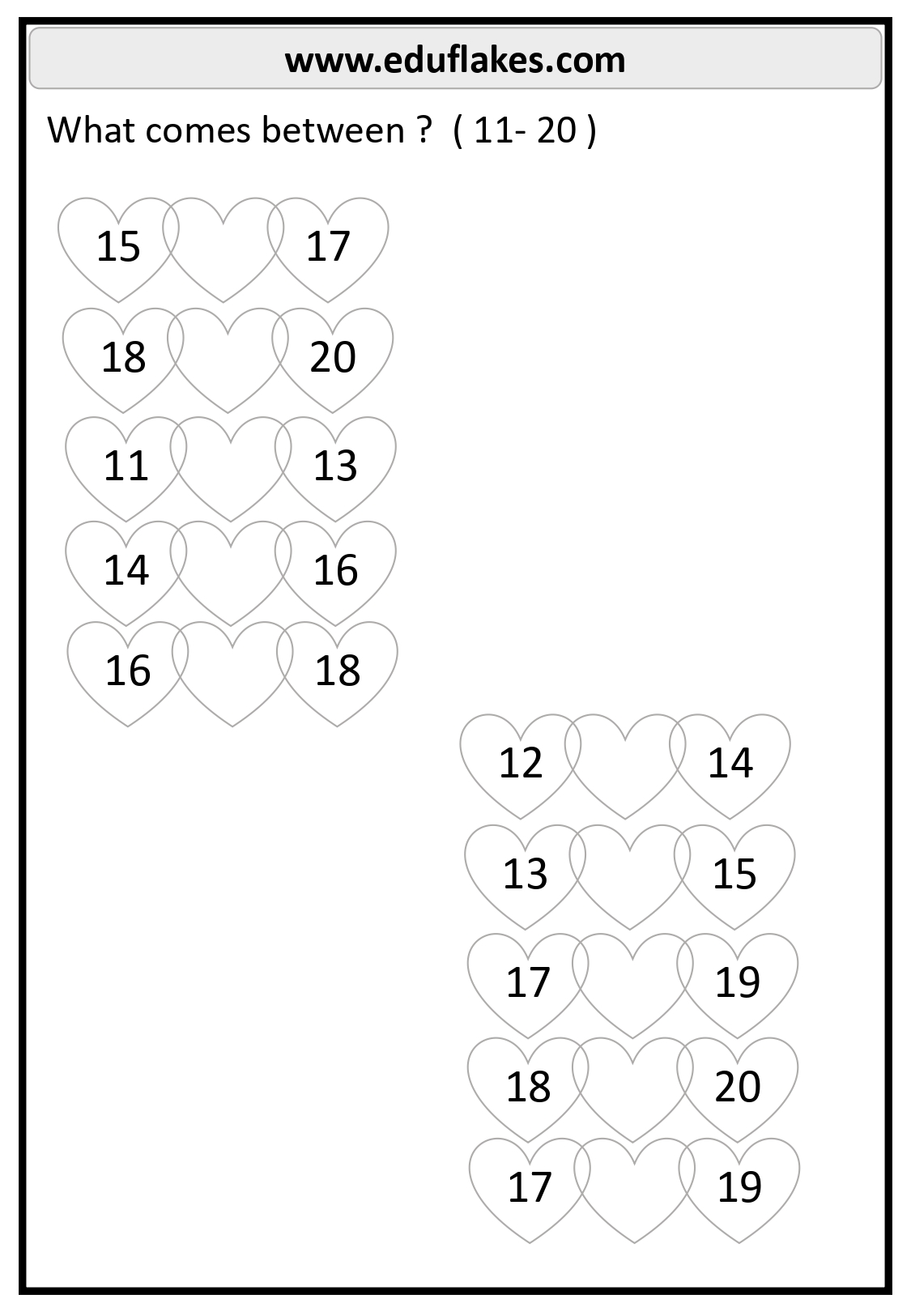
11-20
- Before 15: 14
- After 18: 19
- Between 12 and 14: 13
Beyond 20
- Before 75: 74
- After 108: 109
- Between 31 and 64: (Numbers like 32-63)
Advanced Concepts: Missing Numbers and Patterns
As children master basic number sequences, they can advance to missing number problems and patterns:
- “Find the missing number: 10, __, 12, 13.” (Answer: 11)
- “What comes after 29, 30?” (Answer: 31)
- “What is between 22 and 24?” (Answer: 23)
How Teachers and Parents Can Use This Free PDF
EduFlakes.com provides free, high-quality worksheets to help children grasp number sequencing effectively. Teachers and parents can utilize the provided PDF in various ways:
- Classroom Learning: Print out worksheets and use them in group activities where children can collaborate on solving number problems.
- Home Practice: Parents can engage children in tracing exercises and number-matching games to reinforce learning at home.
- Assessments and Quizzes: Educators can use the sheets for quick assessments to check students’ understanding of number sequences.
- Interactive Activities: Encourage children to use crayons and markers to color the numbers, making learning a fun experience.
- Digital Learning: The PDF can be displayed on tablets or interactive whiteboards for group discussions and problem-solving.
By making use of this resource, educators and parents can provide a structured yet engaging way for children to master number order concepts effortlessly.
Encouraging Independent Learning
To help children become confident with numbers, encourage them to:
- Use number charts for reference.
- Practice daily with real-life situations.
- Challenge themselves with timed exercises and fun quizzes.
Mastering the concepts of before, after, and between is essential for building a strong mathematical foundation. By incorporating number lines, counting exercises, worksheets, daily examples, and games, parents and teachers can make learning engaging and effective. With consistent practice and interactive activities, children will develop a solid understanding of number sequences, preparing them for more advanced mathematical concepts in the future.